Certainly, to implement an efficient ERP is a crucial task; choosing a cloud-based solution can make the process faster. However, since an ERP covers the entire range of business functions, it is important to perform all the necessary steps carefully and methodically.
Switching to a new system, or activating it from scratch, requires a major preliminary analysis, a careful migration and testing process, scrupulous staff training, and fine-tuning of the system.
For this reason, we at Mindquest have summarized the various phases of this process in the following 6 steps.
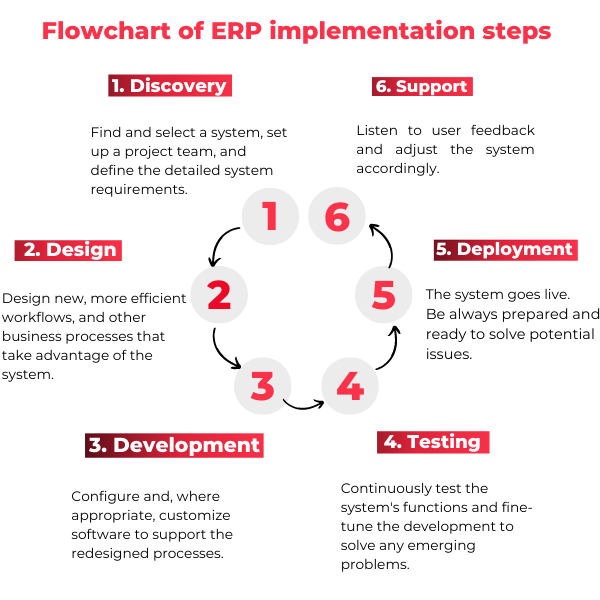
Flowchart of ERP implementation steps
Also read the advantages and disadvantages of SAP
1. Discovery and planning
Firstly, discovery and planning is perhaps the most important phase: if done methodically, it helps reduce time, cost, and risk. This phase consists of researching and selecting a system, establishing a project team, and defining detailed system requirements.
2. Design
Then, by analyzing the hardware and software infrastructure in place, new and more efficient workflows and other business processes can be designed to take advantage of the system.
In particular, if the choice falls to a cloud-based ERP, it is critical to check the quality, stability, and security of Internet access. Systematic analysis of information flows is critical here. Single systems may, in fact, perform less well than industry-specific products.
At this stage, it is also critical to define a team responsible for the process. Since the implementation is a complex task, dedicating resources makes it easier to interface with the support team.
3. Development
In addition of having performed the audit and mapped the information flows, assigned functions and responsibilities, and identified the most suitable solution, the actual implementation phase begins.
This step consists of the configuration of access and permissions. The ERP is used by several users and in different capacities. It is therefore important to set permissions and roles for access according to one’s user profile.
It also includes the preparation of the data and processes to be migrated. Preliminary analysis helps to resolve any format incompatibilities in time. Centralized data management eliminates redundancies and duplicates
4. Testing
During this phase, it is valuable to continuously test the functions of the system and refine the development to solve any emerging problems.
Fine-tuning, it is to say, testing the system to gradually verify the results of the migration process and adjust any discrepancies in use and access.
5. Deployment
Once this phase is also completed, we move on to the actual operational verification of the new ERP. This is accompanied by staff usability testing.
With the new ERP fully operational, it is possible to observe its actual operation. Preliminary analysis and partial testing are useful, but the go-live is the real litmus test.
6. Support
In the initial break-in period, the work of the support and service team is critical. This is also the reason for choosing not only the ERP, but also the company that provides it.
Maintaining the ERP implementation after deployment helps keep users satisfied and ensures that the company achieves the desired benefits.
Last but not leas, the project team may remain responsible for the ERP system during this phase, but will focus on listening to user feedback and adjusting the system accordingly.
Further development and configuration may be needed as new features are added to the system. It is also critical to train new staff on the system to implement an efficient ERP.
Are you looking for freelance or permanent assignments in the ERP field? You can now apply for our Tech & IT job opportunities on our freelance and permanent recruitment platform.
You can also explore the role of the SAP FICO Consultant
Need advice on how to start or develop your freelance consulting business in tech or IT? Need to start a new permanent or freelance assignment? Join Mindquest and get support from our team of experts.

