Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are pivotal for integrating various business processes, enhancing operational efficiency, and facilitating informed decision-making. However, despite their transformative potential, ERP implementations can sometimes falter, leading to wasted resources and unrealized benefits. Therefore, understanding the ERP failure causes and implementing proactive strategies to address them is crucial for ensuring successful adoption and maximizing ROI. In this post, we’ll delve deeper into 10 key ERP failure causes and provide comprehensive solutions to mitigate these risks effectively.
To help companies achieve a successful SAP implementation, this whitepaper explains SAP implementation best practices. It also presents a case study from the global leader sportwear company ADIDAS as an example of successful SAP implementation.
Whether you are a business leader, IT professional, or project manager, this whitepaper will help you understand how to plan, execute, and manage a successful SAP implementation that delivers tangible benefits and ROI.


1. 🗓️ Inadequate Planning and Strategy
One of the first ERP failure causes is an inadequate foundation planning and strategy. This is the main reason why ERP implementations are prone to derailment before they even begin. Rushing into the process without a clear roadmap can result in confusion, delays, and budget overruns.
💡Solution: Prioritize the planning phase by conducting thorough research, engaging key stakeholders, and establishing clear project goals and milestones. Also, develop a comprehensive implementation roadmap that outlines key deliverables, timelines, and resource requirements. By investing time and effort upfront, organizations can set a solid foundation for a successful ERP deployment.
2. ✅ Poor Vendor Selection
Then, second to the list of ERP failure causeschoosing the wrong ERP vendor can spell disaster for an implementation project. Compatibility issues, lack of support, and mismatched expectations can lead to dissatisfaction and inefficiency.
💡Solution: To avoid this pitfall, take a strategic approach to vendor selection by evaluating multiple vendors based on their track record, industry expertise, technological capabilities, and scalability. Engage in thorough due diligence, also including product demonstrations, reference checks, and onsite visits. Moreover, prioritize vendors that demonstrate a deep understanding of your industry and offer a flexible, customizable solution that can adapt to evolving business needs.
3. 🧭 Lack of Executive Support
Moreover, executive buy-in is essential for driving organizational change and overcoming resistance to ERP adoption. Without visible sponsorship and support from senior leadership, ERP initiatives may struggle to gain traction and momentum.
💡Solution: Engage senior executives early in the ERP planning process and clearly articulate the strategic importance of the project. Demonstrate how the ERP system aligns with broader organizational goals, such as improving operational efficiency, enhancing customer satisfaction, or enabling growth opportunities. Secure visible sponsorship from top management to instill confidence in the project and foster a culture of accountability and ownership.
4. 📚 Inadequate Training and Change Management
Also, transitioning to a new ERP system requires a cultural shift and a commitment to ongoing learning and adaptation. Without proper training and change management initiatives, employees may struggle to embrace new processes and technologies.
💡Solution: Develop a comprehensive training and change management program tailored to the specific needs of end-users. Offer hands-on training sessions, workshops, and online resources to familiarize employees with the ERP software and its functionalities. Also, foster a culture of continuous learning and feedback, and provide ongoing support to address user questions and concerns. Then, communicate the benefits of the ERP system transparently and involve employees in the decision-making process to cultivate a sense of ownership and empowerment.
5. 🎛️ Scope Creep
Then, another common reason of ERP failure causes is scope creep: the enemy of ERP projects, leading to ballooning budgets, extended timelines, and diluted focus. Without clear boundaries and prioritization, organizations risk losing sight of their original objectives.
💡Solution: Firstly, define the scope of the ERP project rigorously and establish clear boundaries around deliverables, timelines, and budget constraints. Then, conduct thorough requirements gathering and prioritize functionality based on business value and impact. Also, resist the temptation to accommodate every stakeholder request and focus on delivering core functionalities that address critical business needs. Regularly review and reassess the project scope to ensure alignment with evolving business priorities and market dynamics.
6. 📊 Poor Data Quality and Governance
Also, data is the lifeblood of ERP systems, and poor data quality can undermine their effectiveness. Without proper governance and data management practices, organizations risk making decisions based on inaccurate or incomplete information.
💡Solution: Prioritize data quality initiatives as part of the ERP implementation process, including data cleansing, validation, and enrichment. Establish robust data governance policies and procedures to define data ownership, access controls, and quality standards. Invest in data management tools and technologies to automate data validation. Enforce data governance policies, and maintain data integrity throughout the ERP lifecycle. Regularly monitor and audit data quality metrics to identify and address issues proactively.
Learn more about the advantages and disadvantages of SAP
7. 📝 Overlooking Integration Challenges
In addition, ERP implementations often require integrating with existing systems and processes. Ignoring integration challenges can result in data silos, workflow disruptions, and compatibility issues.
💡Solution: Conduct a thorough analysis of integration requirements early in the ERP planning process to identify potential bottlenecks and dependencies. Engage cross-functional teams, including IT, operations, and business stakeholders, to collaborate on integration design and testing. Leverage integration tools, middleware solutions, and industry standards (e.g., APIs, web services) to facilitate seamless data exchange and interoperability between disparate systems. Prioritize data mapping, transformation, and validation to ensure consistency and accuracy across integrated systems.
Also read the 5 key benefits of hiring a SAP FICO Consultant
8. 🔬 Insufficient Testing
Then, thorough testing is essential to uncovering software defects and usability issues before they impact end-users. Without adequate testing, organizations risk encountering critical issues during production deployment.
💡Solution: Develop a comprehensive testing strategy that encompasses functional testing, regression testing, performance testing, and user acceptance testing. Define test scenarios, scripts, and acceptance criteria based on business requirements and user workflows. Allocate sufficient time and resources for testing activities throughout the ERP implementation lifecycle, including system configuration, customization, and data migration phases. Leverage automated testing tools and methodologies to accelerate testing cycles, improve test coverage, and identify defects early in the development process. Encourage user participation in testing activities to validate system functionality, usability, and performance from an end-user perspective.
9. 🤝 Failure to Align with Business Processes
Also, ERP systems should align with existing business processes to maximize efficiency and effectiveness. Failure to map ERP functionality to business requirements can lead to resistance and inefficiency among end-users.
💡Solution: Conduct a thorough analysis of existing business processes and identify opportunities for process optimization and standardization. Engage key stakeholders, including department heads, process owners, and end-users, to collaborate on business process mapping and requirements gathering. Customize the ERP system to align with specific business needs and industry best practices while minimizing the need for complex customizations. Provide training and support to help users understand how ERP functionality supports their day-to-day tasks and decision-making processes. Continuously monitor and refine business processes based on user feedback, performance metrics, and industry trends to drive continuous improvement and organizational agility.
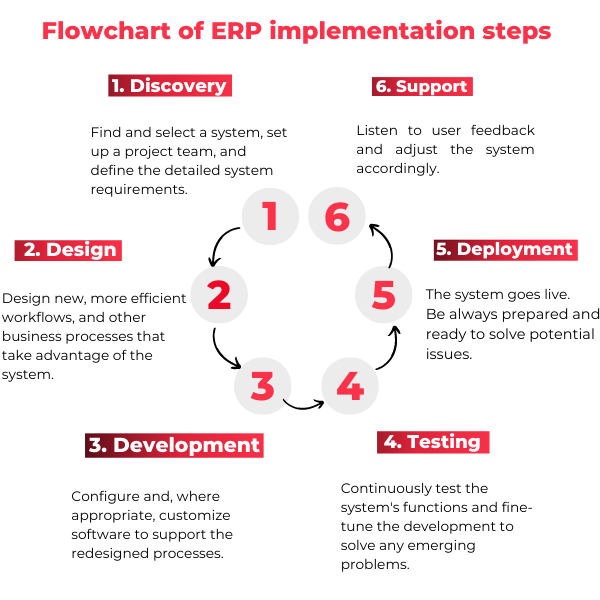
Also read how to implement an efficient ERP in 6 steps
10. 🛠️ Lack of Ongoing Support and Maintenance
Lat but not least, ERP implementations require ongoing support, maintenance, and updates to remain effective over time. Without dedicated resources and processes in place, organizations risk encountering technical issues and compliance challenges.
💡Solution: Establish a dedicated support team or center of excellence (CoE) responsible for managing ERP system operations, maintenance, and user support. Define service level agreements (SLAs) and escalation procedures to prioritize and address user queries, technical issues, and enhancement requests in a timely manner. Invest in training and knowledge transfer to empower internal resources to handle routine support tasks and troubleshoot common issues independently. Stay informed about software updates, patches, and security advisories released by the ERP vendor and apply them promptly to mitigate security risks and ensure regulatory compliance. Continuously monitor system performance, usage trends, and user feedback to identify opportunities for optimization and enhancement. Engage with the ERP vendor and user community to stay abreast of best practices, industry trends, and emerging technologies that can further enhance the value and capabilities of the ERP system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ERP failure causes can be attributed to a myriad of factors, including inadequate planning, poor vendor selection, lack of executive support, and insufficient training and change management. However, by addressing these challenges proactively and implementing best practices for ERP implementation and management, organizations can minimize risks, maximize ROI, and achieve long-term success with their ERP initiatives. By fostering a culture of collaboration, innovation, and continuous improvement, organizations can leverage ERP systems as strategic enablers of business transformation, growth, and competitive advantage.
Need advice on how to start or develop your freelance consulting business in tech or IT? Need to start a new permanent or freelance assignment? Join Mindquest and get support from our team of experts.