SAP FICO (Finance and Controlling) is a critical module within the SAP ecosystem, as it helps businesses efficiently manage their financial processes while ensuring compliance. So, to gain the necessary skills for managing financial transactions, analyzing business performance, and adhering to regulations, SAP FICO training is essential. Whether you aim to advance your career or enter the SAP consulting world, mastering SAP FICO is crucial. Consequently, in this article, we will explore some of the top SAP FICO courses and certifications that can help you succeed in this ever-evolving field.
Need advice on how to start or develop your freelance consulting business in tech or IT? Need to start a new permanent or freelance assignment? Join Mindquest and get support from our team of experts.

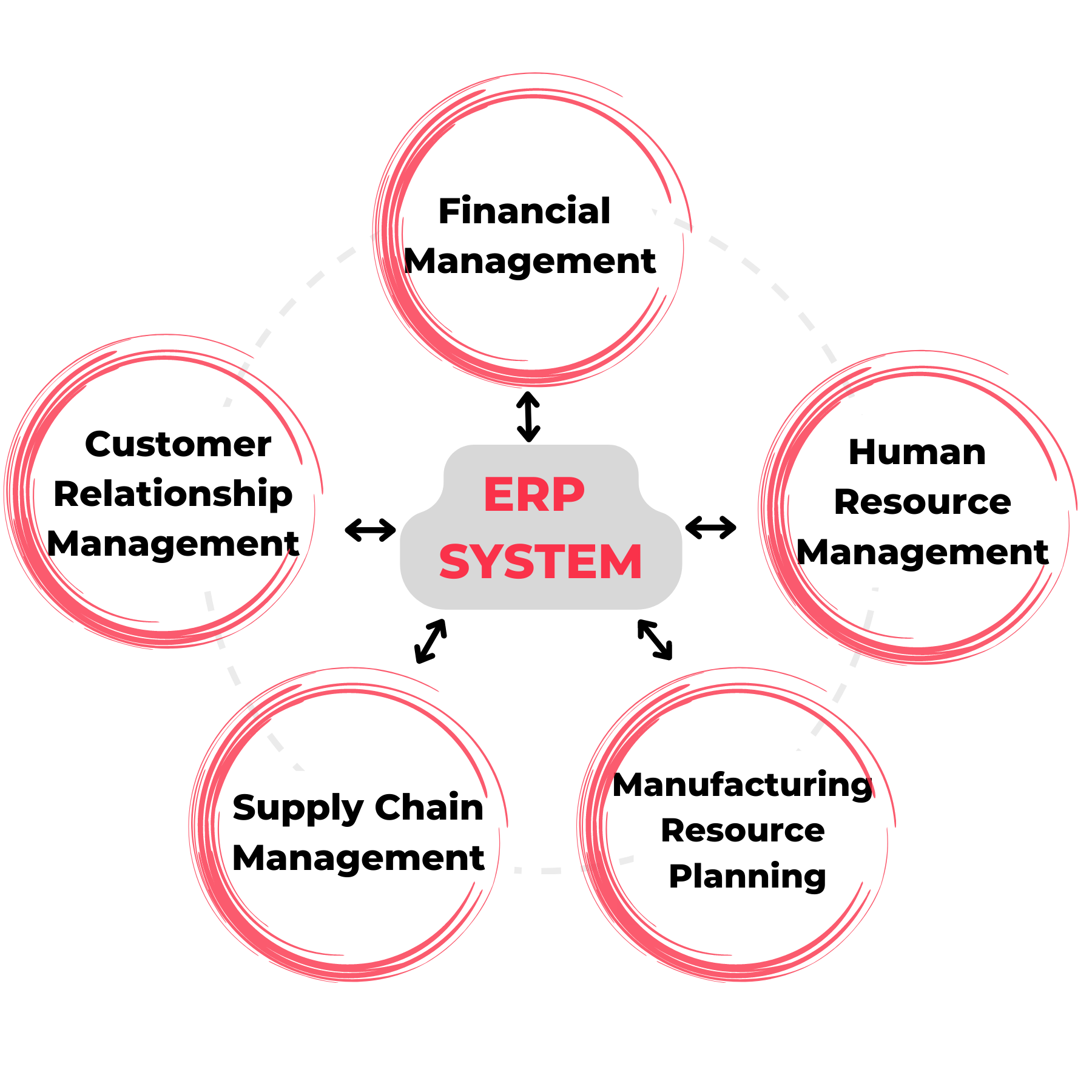
What is SAP FICO?
SAP FICO (Finance and Controlling) is one of the most widely used modules within SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing). Thus, it enables businesses to manage and monitor their financial transactions effectively. Moreover, it integrates both financial accounting and controlling functionalities, thereby allowing organizations to track and analyze financial data efficiently. This integration facilitates informed decision-making.
SAP FICO plays a crucial role in several areas, including:
- Managing financial data
- Analyzing performance
- Supporting strategic decision-making
- Ensuring regulatory compliance
1. Financial Accounting (FI)
Firstly, the SAP Financial Accounting (FI) module deals with general accounting and financial operations within an organization. This module is also indispensable for monitoring and controlling financial transactions and ensuring regulatory compliance. Additionally, it assists in managing key functions such as:
- Accounts receivable and payable
- Asset accounting
- Cash and liquidity management
- Debt and credit management
- Preparation of financial statements, including balance sheets and income statements
2. Controlling (CO)
In contrast, the SAP Controlling (CO) module focuses on managerial accounting and performance management. Thus, it provides detailed insights into cost management, product profitability, and performance, thereby enabling organizations to control operations more effectively. The CO module is essential for tracking:
- Production costs
- Profitability of products and projects
- Service and support cost controls
- Planning and budgeting future activities
3. Integration and Analysis
Then, one of SAP FICO’s standout features is its seamless integration with other SAP modules such as procurement, inventory management, production, and sales. This integration, therefore, allows for a comprehensive view of business operations, making it easier to analyze financial performance and make data-driven decisions.
Best SAP FICO Training Options for Consultants
Also, there are several SAP FICO training programs available for professionals who want to gain expertise in this module. Below are some of the top training options.
But first, let’s answer some of the most common questions about SAP FICO training.

- How much does SAP FICO training cost?
Firstly, the SAP certification cost can vary based on the location, duration of the program, and the level of SAP certification you are aiming to achieve.
- Is SAP Fico easy to learn?
The question of whether it is hard or easy relies completely on the person’s commitment and interest in learning. Hard work is key to successfully learning any new skill or acquiring knowledge.
- Is Sap Fico a good career?
A career in SAP FICO is very good and demanding, and it continues to grow. The popularity and demand for SAP are increasing day-by-day throughout the world. Moreover, SAP FICO offers you a great number of career options within its domain.
- What is the SAP FICO Course Duration?
The SAP FICO online course duration is about 3 months.
- Why should I go for SAP FICO Training?
Enrolling in SAP FICO training can offer you numerous high-paying job opportunities.
- Who will teach the SAP FICO Course?
You will be providing SAP FICO working professionals with more than 10 years of experience in this domain.
- Does SAP FICO require coding?
Contrary to certain other SAP modules, SAP FICO Course normally doesn’t require advanced coding abilities.
Now that you solved all your doubts about SAP FICO trainings, you can delve into the top SAP training options:

1. Official SAP FICO Training by SAP
SAP offers official training courses, both online and in-person, for professionals at various levels. These courses, delivered by certified SAP instructors, cover everything from foundational concepts to advanced functionalities. Consequently, to explore the available training programs, visit SAP’s official training website.
2. Online SAP FICO Training Platforms
In addition to official SAP courses, many online learning platforms provide SAP FICO courses. Some of the most popular platforms include Udemy, Coursera, LinkedIn Learning, and Pluralsight. When selecting an online course, it is important to choose one led by experienced instructors and to review student feedback to ensure quality.
3. SAP FICO Training at Specialized Training Centers
Alternatively, many organizations specialize in SAP training and offer intensive classroom-based courses. These programs offer hands-on experience and provide an opportunity to interact with instructors and peers. Therefore, for in-person learning, consider finding reputable training centers in your region.
4. University Courses
Also, some universities offer SAP FICO training as part of broader management or information systems degrees. These courses can provide a more academic and thorough approach to SAP FICO. For instance, Poitiers University and Tours University in France offer SAP-related courses that are highly regarded.
5. In-house Training
If your organization already uses SAP, it is worth checking whether they offer internal training programs for SAP FICO. This option can be especially beneficial as in-house training is often tailored to meet your company’s specific needs and processes. Consequently, reach out to your HR or IT department to explore potential opportunities.
Top 3 SAP FICO Certifications for SAP FI CO Consultants

If you’re looking to advance your career or gain new qualifications as an SAP FI CO consultant, several well-recognized and highly valued certifications are available. Below are five of the top certifications you should consider:
1. SAP Certified Application Associate – SAP S/4HANA Cloud – Finance Implementation
This certification focuses on SAP S/4HANA Cloud Finance, covering the essential skills needed to implement and manage financial processes within the cloud environment.
2. SAP Certified Application Professional – SAP S/4HANA for Financial Accounting Associates
This certification is designed for experienced finance professionals and emphasizes advanced features of SAP S/4HANA Financial Accounting, including complex configurations and operations.
3. SAP Certified Application Associate – SAP S/4HANA for Management Accounting Associates
This certification is ideal for professionals specializing in SAP Management Accounting (CO) within the S/4HANA environment, focusing on cost management and performance analysis.
Final Tips for Success
Before attempting any certification, it’s essential to gain practical experience and complete the relevant training courses. Additionally, engaging in real-life projects and exercises will help reinforce your understanding and improve your chances of passing certification exams.
For more information on available certifications and training programs, be sure to explore the Mindquest SAP Community. Here, you’ll find the latest insights, job opportunities, and resources tailored for SAP professionals.
In conclusion, SAP FICO training and certifications offer excellent career growth opportunities. By carefully planning your learning path and gaining practical experience, you can position yourself as a sought-after consultant in the SAP ecosystem.
Find your next assignment on our freelance and permanent IT recruitment platform, or join Mindquest so you don’t miss out on any job opportunity!